CBT Techniques, Worksheets And Q&A | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive-behavioral therapy exercises for anxiety is a popular and effective therapeutic approach to help you manage your symptoms.
If you have anxiety, there are a few methods that can be used to help alleviate your symptoms:
- Writing therapy. Writing therapy exercises help you be aware of the sources and triggers of anxiety and identify ways to cope with them.
- Exposure therapy. In this therapy, you are exposed to a particular situation that tends to trigger your anxiety. You are encouraged to control yourself and not react to the situation and write about how you feel.
- Visualization therapy. Visualize or imagine the situation that causes you severe anxiety and play it out in your head from start to end. This will help you understand that no matter what happens, you will be okay. This constant visualization desensitizes you overtime to the situation.
Listen to the Podcast
Doing these few therapy methods will significantly help you. Read on to learn about more strategies to reduce your anxiety symptoms even further.
Products We Recommend For Anxiety
- Weighted Blanket
- Aromatherapy Essential Oil Diffuser
- Essential Oils
- Anti-Stress Gummies
- Happy Light Therapy Lamp
- Calming Scented Bath Salts
- Self Care Gift Set
- Yankee Candle Lavender Calming Scent
According to the latest research, anxiety disorders are among the most common illnesses in the United States of America. Every year 40 million adults report suffering from symptoms of anxiety.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Exercises
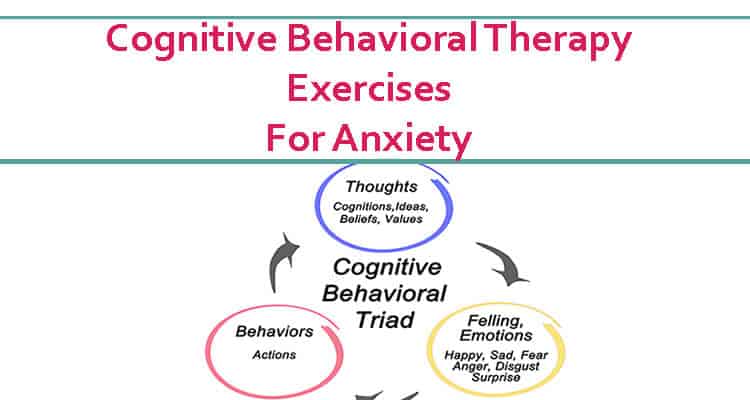
Anxiety disorders develop from a culmination of factors, such as genetics, brain chemistry, life events, and personality.
Psychology Today, a renowned psychological magazine, defines Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) “As a form of psychotherapy that treats problems and boosts happiness by modifying dysfunctional emotions, behaviors, and thoughts.
Unlike traditional Freudian psychoanalysis, which probes childhood wounds to get at the root causes of conflict, CBT focuses on solutions, encouraging patients to challenge distorted cognitions and change destructive patterns of behavior.”
Cognitive-behavioral therapy is based on the principle that your thoughts, attitudes, and beliefs significantly affect your behavior and that mental disorders like anxiety and depression can effectively be dealt with by changing your negative thought processes.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy compares our thinking pattern to a pair of glasses that enables us to view the world differently. If our thinking is positive, we will have a positive outlook on life, and if our thinking is negative, we will have a negative view of the world.

Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
According to the founder of cognitive-behavioral therapy, Dr. Aaron T. Beck, “The perceptions and interpretations of a depressed person are distorted, causing him/her to engage in “cognitive errors” such as a negative mindset, jumping to conclusions, catastrophizing and thinking only in black and white.”
Beck noted that these thoughts came automatically to the individual causing him/her to believe them as absolute truths instead of distortions, leading to mental disorders like anxiety, depression, phobias, etc.
Cognitive behavior therapy exercises for anxiety focuses on modifying these negative thought patterns by challenging them against reality.
When individuals replace these negative and harmful thoughts with positive thinking, their anxiety and distress levels considerably reduce, allowing them to function normally.
According to psychologist- Grohol (2016), these inaccurate thoughts and belief systems that reinforce negative behaviors, thought patterns, and emotions are called Cognitive Distortions.
Cognitive distortions alter our vision from the truth, and we all experience them at some point in our lives. When these distortions take over an individual’s thought processes, it leads to mental disorders like anxiety attacks, extreme feelings of despair, hopelessness, and doom.
Related Post: Essential Oils For Anxiety And Panic Attacks
What this video: Daily CBT Techniques
Distortions Affecting Your Thoughts
There are 15 types of distortions that affect one’s thought processes and are the significant causes of anxiety.
1. Filtering: Filtering refers to the distorted thinking of an individual who chooses to dwell only on their life’s negative happenings, ignoring all the positive occurrences.
Even though many good things may happen in the person’s day, the individual may focus only on negative happenings, thus increasing anxiety levels.
2. Polarized or Black and White thinking: As the name suggests, this distortion is all about thinking in black or white, with no grey shades in between.
For example, if a student is weak at a particular subject, he/she may believe “that they are a failure and will not be able to succeed in their life” even though they may be useful in other subjects in reality.
This kind of thinking leads to a sense of despair, eventually increasing one’s sense of anxiety.
3. Overgeneralization: When overgeneralizing, an individual may tend to make decisions based on the occurrence of one or two events. For example, if a man fails in an interview, he may conclude that he would “always” fail “every” interview and “never” succeed.
The words “every,” “never,” and “always” are often mentioned in overgeneralized statements. This kind of negative self-talk leads to low self-esteem and high anxiety levels in an individual.
4. Jumping to Conclusions: Jumping to conclusions refers to making a decision about someone or a situation without considering all the facts and evidence. E.g., statements like “All men are unfaithful,” “She hates me because I am a good student” are examples of this distortion.
This distortion negatively impacts the individual’s relationships, causing him/her to be isolated from others.
Also, judging situations and people’s mental strain tends to take a toll on one’s mind, causing an individual to become more anxious and susceptible.
5. Catastrophizing / Magnifying or Minimizing: Also known as the binocular trick, this distortion refers to an individual’s tendency to blow things out of proportion by expecting the worst to happen.
E.g., the individual may make a small mistake in their exams and conclude that they should quit school. The other extreme form of this distortion is minimizing one’s positive characteristics or overlooking another’s imperfections.
The best example quoted for this situation is when an individual is in an abusive relationship.
The abused tends to minimize their self-worth and overlook their abuser’s imperfections ultimately. This distortion leads to wrong decision making, eventually leading to high anxiety levels.
6. Personalization: Personalization occurs when an individual holds themselves unreasonably responsible for the occurrence of an unpleasant event. They may believe that it is either something they have done or have not done that has led to the event’s happening.
E.g., A woman may think that she had a horrible day because she walked out of the front door instead of using the back door.
This distortion causes an individual to get worked up about many unrealistic things, thereby increasing their anxiety levels.
7. Control Fallacies: Human beings like to have a sense of control over what is happening in their lives. Sometimes things happen in our life, which is beyond our control.
In this distortion, however, an individual may have the mistaken belief that either he/she is solely in control of others’ happiness and sense of well-being. Or that others are responsible and in control of their happiness.
The individual either burns themselves out with unrealistic efforts to make others happy or are filled with extreme resentment about others not doing enough to keep them happy.
These unrealistic demands both from oneself and from others greatly enhance one’s anxiety levels.
8. The Fallacy of Change: The unrealistic belief that others should act in accordance with one’s wish and fancy is called the fallacy of change.
This distortion is a source of unpleasantness in the individual’s life and the lives of the significant people around him/her.
9. The Fallacy of Fairness: Life is not fair at all times, and what seems reasonable to one person may seem very unfair to the other.
An individual suffering from this distortion may find it very hard to accept this fact. In turn, it may cause feelings of resentment and despair, causing the individual to suffer from anxiety.
10. Heaven’s reward fallacy: This fallacy refers to the distortion where an individual believes that all their sacrifice, self-denial, and righteous actions are watched by a higher power and will be rewarded.
A sense of despair and unhappiness seeps in when the rewards don’t come, thus making the person very anxious.
11. Should or Should Not’s: This distortion is characterized by statements of “Should and Should not’s,” which are internalized rules that govern the individual’s behavior.
If the individual goes against them, they are plagued with guilt, and if others go against them, the individual experiences annoyance and resentment. This irrational thinking is a great source of anxiety for the individual.
12. Emotional Reasoning: This distortion causes the individual to believe that what he/she is feeling is the absolute truth.
This irrational belief system causes them to experience increased feelings of anxiety and unworthiness. E.g., If a woman feels ugly and disinteresting, she may believe that she is genuinely unattractive and not worthy of being admired.
13. Global Labelling/Mislabeling: This distortion is a form of false thinking wherein individuals exaggerate, generalize, and label themselves, situations, or other people without knowing the entire truth.
This kind of thinking leads to a lot of prejudice and misunderstanding and can be a cause of unhappiness in the person’s life, leading to anxiety.
14. Always being Right: In this distortion, the individual considers themselves to be always right. They can go to any extent to prove their point.
This kind of thinking can be tiring and can be regarded as selfish and narcissistic. It causes a lot of mental strain on the individual as they are continually trying to prove themselves.
15. Blaming: Anxiety builds up in an individual due to this distortion because they believe that others are to blame for their unhappiness.
They don’t feel the need to take responsibility for their happiness and suffer from discontentment.
Individuals suffering from the distortions mentioned above consider their false beliefs real and their lives’ absolute truth. It is causing them to suffer from anxiety and various other mental disorders.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy exercises for anxiety are an excellent method to help these individuals. The therapy uses positive self-talk, reasoning, and the following techniques to help alter an individual’s distortions.
Therapy methods can be classified into the following types

Writing Therapy
- Journaling: Journaling therapy is an important form of writing therapy. It requires you to write down your thought processes honestly, feelings, and emotions.You describe why you feel a particular way and write a detailed description of the intensity of their thoughts and emotions. This therapy exercise helps you be aware of the sources and triggers of anxiety and identify ways to cope with them.
- Pleasant Activity Scheduling: You can do this writing activity with/without the help of a therapist. This activity requires you to write down at least one event per day you would engage in throughout the next week.Writing down these activities gives a sense of accomplishment and brings about more positivity in your day.
- Situation Exposure Hierarchies: This therapeutic exercise requires you to write down situations that cause you stress and increase your anxiety. Then you rate the level of distress (on a scale of 0-10) you feel regarding each situation.Once assessed, then you’ll be asked to rank them by their distress rating. This gives you an idea about the issues you need to address first. This writing technique is used when someone is unsure about what causes them so much anxiety.
- Writing down Self Statements: Here, you will write down counteractive statements to the negative thoughts you think. This therapy helps overcome negative thought patterns with positive affirmations. E.g., an individual who feels useless can think, “I am an intelligent and creative being.”
Related Post:7 Signs Your Anxiety Is Out Of Control

Exposure Therapy
- Exposure and Response Therapy: In this therapy, you are exposed to a particular situation that triggers obsessive behavior. You are then encouraged to control yourself and not react to the situation and write about how you feel. This therapy is beneficial for individuals suffering from Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.
- Interoceptive Exposure: This therapy technique involves exposing you to feared bodily sensations similar to those experienced during panic and anxiety attacks. The fear of experiencing these symptoms causes the individual who suffers from them to become withdrawn and isolated. This is to help you overcome your concerns and be better equipped when in a similar situation.
- Nightmare exposure and rescripting: This therapy technique is useful for those individuals who suffer from recurrent nightmares. This therapy requires the client to discuss their nightmares and the negative emotions associated with them. The therapist then addresses alternative and positive images to accompany the dreaded feelings, thus reducing the nightmares’ fearfulness.

Visualization Therapy
- Play the script until the end: This therapeutic technique is used when someone suffers from crippling fear or extreme anxiety. You visualize or imagine the situation that causes severe anxiety and play it out in your head from start to end. This helps you understand that no matter what happens, everything will turn out to be okay. This constant visualization desensitizes you slowly to negative emotions and enables you to overcome anxiety.
- Thought Records: This therapy technique, according to Boyes, applies the use of logic to ward off irrational negative thoughts and replace them with more balanced and rational thoughts.
- Imagery Based Exposure: In this therapy technique, you are asked to call to mind a recent memory that produced strong negative emotions and analyze the situation. Think about “what happened,” “what you felt,” “how you felt like reacting to the negativity,” and label the various emotions you experienced. This is done repeatedly until the situation no longer has the power to trigger negative emotions.

Behavior Therapy
- Meditation: In this therapeutic technique, the individual is guided to consciously turn their attention from distracting thoughts and feelings and focus on the present moment. According to researchers, this therapy form is a great way to reduce anxiety.
- Deep Breathing: This therapy technique can be closely associated with mindful meditation, wherein the client is asked to focus on taking deep and relaxed breaths. Focusing on one’s breathing helps grab the attention away from one’s anxious thoughts, thus improving the individual’s sense of calm and balance.
- Behavior Experiments: According to psychologist Boyes, behavior experiments are a therapeutic technique wherein the client tests the “what ifs” practically outside their thoughts.
E.g., A person who feels anxious to sing publicly can tell themselves, “If I sing, everyone will think I sound bad vs. If I sing, everyone will think I have a good voice.”
By witnessing the outcome, the individual gets to understand the rationality of their thoughts.
The above mentioned cognitive behavioral therapy exercises for anxiety help a client achieve positive behavioral goals when practiced faithfully.
Anxiety is not a disease but a mental condition that can be effectively resolved with a therapist’s help. If you find yourself suffering from the distortions mentioned above, do not hesitate to seek advice.

CBT Worksheets – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Worksheets
- Alternative Action Formulation
- Functional Analysis
- Longitudinal Formation
- Dysfunctional Thought Record
- Fact or Opinion Worksheet
- Cognitive restructuring
Alternative Action Formulation: A therapist uses this therapy technique to guide their clients through anxiety treatment and understand their thoughts’ rationality. This therapy form administered in the form of a worksheet wherein the client has to:
- Make a note of all their problems.
- Identify the reasons why they and not others are prone to suffer from these problems.
- Thirdly, make a note of the ways they can cope with these problems.
- Then assess the long-term effectiveness of these coping strategies and
- Finally, the client is asked to note down alternative routes to follow if the coping strategies don’t work.
Functional Analysis: The ABC model also helps the client identify negative behaviors that are ruining their life and come up with solutions to modify them. The sheet is categorized under three headings-
- Antecedents: The client is required to make a note of factors that led up to the “Behavior that requires to be changed.”
- Behaviors: Under this heading, the client has to write down all the actions that need to be changed and why they need to be replaced.
- Consequences: Here, the client has to write about the effects of the questioned behavior and how it affects their life.
Longitudinal Formation: This detailed worksheet addresses 5P’s- these are factors described below that help an individual get a good understanding of their core beliefs, thought patterns, and present behavior. The client needs to fill in the information under each factor accurately.
- Presenting: Events that lead to undesired behavior
- Predisposing: All experiences from childhood that led to the behavior.
- Precipitating: Beliefs they have about this behavior.
- Perpetuating: Internal rules they adhere to when thinking or behaving.
- Positives: The results, whether positive or negative when they behave per their internal rules.
The client then has to continue to introspect and write down the following information.
- Behavior and Feelings: The client must think of a situation that brings about negative thoughts and note down the action, feelings, and physical reactions it brought out.
- Protective Factors: The client is then required to list down ways to help them deal with their negative thoughts and behaviors.
- New Rules for Living: Finally, the client has to make a list of new rules for themselves to break the cycle of negativity and lead a better life.
Dysfunctional Thought Record: A therapist uses this worksheet to help a client who suffers obsessively from negative thoughts. This worksheet divided into seven columns where the client is required to write down the following:
- Date and time the thought arose
- The situation that led to it
- The feeling that came up
- The emotional reaction that followed – Here you would identify false beliefs and opinions with a type of cognitive distortion (described above).
- Write down alternative thoughts that can replace irrational thoughts.
- And finally, the outcome of this exercise.
Fact or Opinion: The therapist uses this worksheet to help clients distinguish facts from their own beliefs. The therapist helps the client understand the difference by challenging the client’s views against the truth. This worksheet consists of 16 statements that the client has to distinguish as fact or opinion.
Cognitive restructuring: This worksheet based therapeutic technique helps individuals suffering from irrational thoughts challenge and question their views. The client must note down the “Thoughts to be questioned” and write down evidence for and against these thoughts; the client then must identify if these thoughts are facts or judgments.
- Next, the client distinguishes if it is an absolute truth or if there is an area of grey in between. Finally, the client has to decide if the thought is valid or just an assumption. This therapeutic technique can be done in a verbal exchange between the therapist and the client.
Can I do cognitive behavioral therapy on my own?
Yes, you can do CBT by yourself. Most people don’t have access to a CBT therapist; maybe they’re not close to one or are not in the network, and self-directed CBT can help anxiety and depression when CBT techniques are used.
Studies have shown people didn’t see a 100% improvement but felt noticeably less anxious and depressed.
A good book called – Retrain You Brain: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in 7 Weeks and this list of books can help you on your way to lowering your anxiety levels.
What happens in CBT sessions?
While in session, your therapist will help you break down your problems into smaller separate parts, such as your physical feelings, thoughts, and actions.
How long does it take for cognitive behavioral therapy to work?
A CBT course of treatment usually lasts between five and twenty sessions, depending on the severity of symptoms. Each session will last between thirty and sixty minutes.
What is the success rate of cognitive-behavioral therapy?
CBT is the most effective treatment for people with anxiety and depression and is 50-75% effective after 5-15 sessions.

It would be great if a person could click into the visualization therapy picture and have a short introductory visualization (30 second – 1 minute).
Maybe your links aren’t working? Or they aren’t set up to take people to an example, or other links?
CBT WORKSHEETS
EXPOSURE THERAPY
WRITING THERAPY
I do like your site 🙂 I think it would be fabulous if you offered just a little more.
Thanks for the comment and input Jonella! I’ve created a few CBT worksheets that can be downloaded, printed and used. More to come soon.
Brilliantly written and set up. Thank you very much, just reading this has helped me already.
Concisely written.
I am not sure if I have anxiety or depression, but following a cancer diagnosis two years ago, I remembered a particular set of events that happened forty years ago, and have since played and replayed every aspect of the event. Obviously I did not deal with this well at the time (in fact buried it deeply. ) I feel that I can cope with the actual events, but need a way to stop replaying it. It’s as if my thoughts are stuck in a loop. Would cognitive behavioural therapy help me or would you suggest some other technique. Thank you.
Hi Donna! Cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT, is a short-term therapy technique that can help you find new ways to change your thought patterns. Engaging with CBT can help reduce stress, cope with grief, complicated relationships and deal with common life challenges.
CBT is very effective for anxiety and is an effective psychological treatment for moderate and severe depression. I wish you well!
I think this series of types of therapy was very helpful to me. I am receiving therapy for the last 5 or more years and I see the distorted thinking I have of people which is so detrimental to the individual to be a whole person! Thank you all for putting all this info out on Pinterest. It made me think a lot about my anxieties and fears. I live in a seniors Retirement Home and I am younger than most of the people here. In reading your studies I realized how distorted my thinking has become and how I view the people here and see them as demented, mentally ill, very aged and needing more care -giving. I have come to the realization that my FAITH has brought me to a point of Compassion for these folks & I should not disdain them! I continue to use my Faith beliefs as well as therapy combined to help myself be a better person. Thank you for giving me the chance to express my views here.
Thanks for sharing Marion, I wish you well!
I love your podcast and information on treatment of anxiety. Very calming and uplifting ! Thank you!